Understanding the Stages of Gum Disease
 Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that causes inflammation and bone loss around the teeth. The bacteria breed in the plaque and tartar that naturally accumulate around the gum line. If the plaque is not routinely removed through daily hygiene and regular dental cleanings, gum disease can progress, resulting in more serious issues such as tooth loss.
Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that causes inflammation and bone loss around the teeth. The bacteria breed in the plaque and tartar that naturally accumulate around the gum line. If the plaque is not routinely removed through daily hygiene and regular dental cleanings, gum disease can progress, resulting in more serious issues such as tooth loss.
Our doctors at The Smile Center in Virginia Beach, VA provide treatments that can eradicate infection-causing bacteria for a healthier smile. Here, we discuss the different stages of gum disease, and how to maintain optimal periodontal health.
Gingivitis
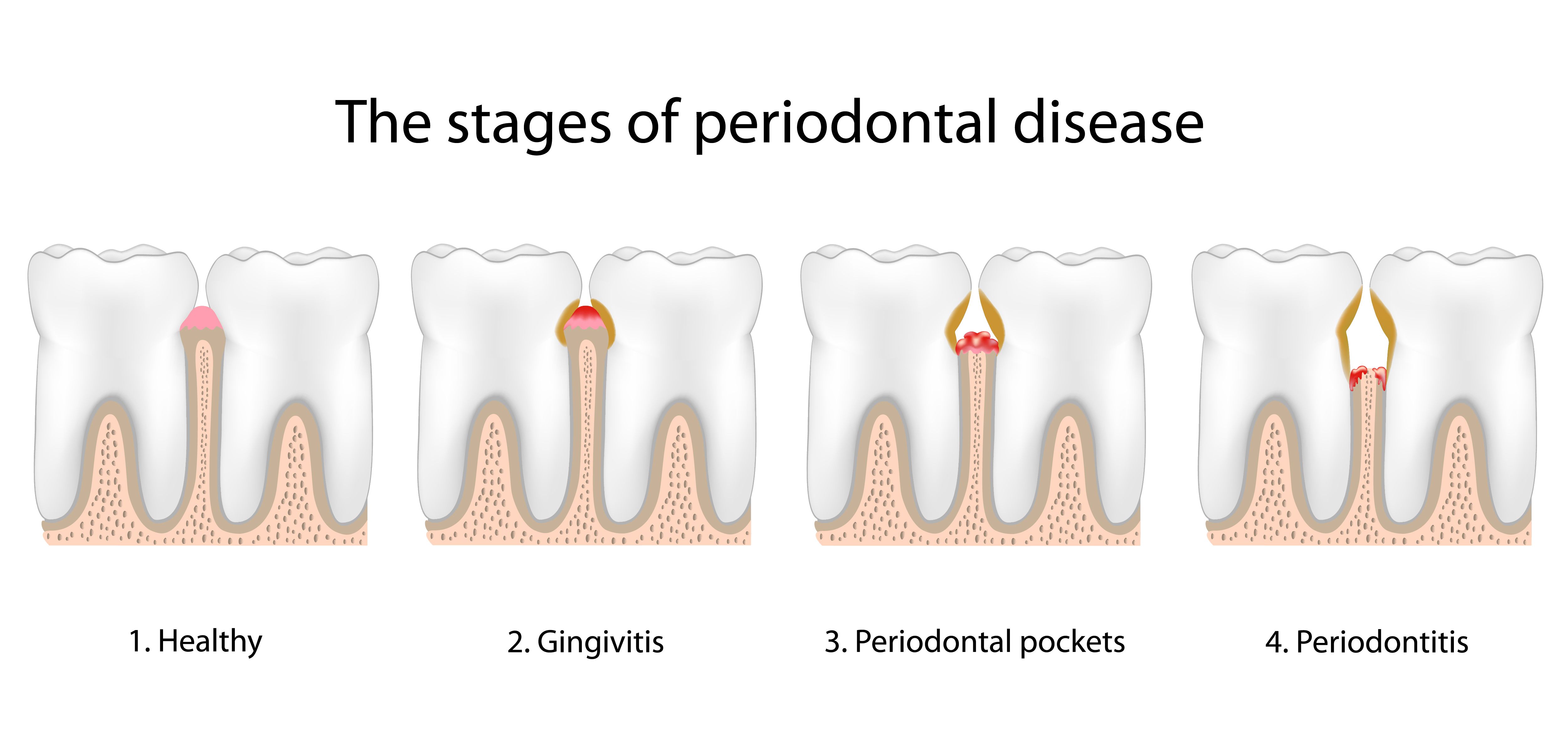
Gingivitis can be considered the warning sign of periodontal disease. During this early stage, toxins cause the gums to become puffy, red, and inflamed. Many patients with gingivitis will experience bleeding when brushing and flossing. During this stage, the underlying bone and surrounding connective tissues are still intact. Therefore, gingivitis is reversible.
Often, treating gingivitis is as straightforward as making improvements to your daily hygiene regimen. Brushing at least twice per day and flossing at least once per day can successfully remove plaque around the teeth. A dental cleaning can also be beneficial to jump start your routine and help you stay on the right track. It is important to note that you should not avoid brushing or flossing if your gums are bleeding. Rather, you should become more aggressive to combat the plaque and bacteria that are causing your gums to bleed in the first place. After a couple weeks of diligent care, the bleeding will lessen, and the gums will become pink and healthy again.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress into periodontitis. During this stage, the plaque around the teeth can harden and become impacted below the gum line. The bone and tissue that support your teeth become compromised, and pockets may form around the roots. Once the pockets are present, further food, debris, and plaque can build up, perpetuating the cycle. The gums can also separate from the teeth, leading to recession.
Non-surgical treatments are helpful in treating mild to moderate periodontitis. At our practice, this often includes scaling and root planing and laser therapy. During treatment, the plaque and tartar will be removed, and the roots of the teeth will be smoothed to discourage further plaque from reattaching. Laser therapy can target infected tissue and leave healthy tissue intact, effectively sterilizing the pockets around the teeth.
Advanced Periodontitis
The final stage of gum disease is aggressive periodontitis, in which the gum tissue and bone around the teeth are destroyed. This can result in shifting or mobility, which can cause serious changes in your bite.
In some cases, surgical intervention can clean out the bacteria and stabilize the teeth. However, if treatment is not successful, the teeth will need to be removed.
The Importance of Periodontal Maintenance
The best way to prevent gum disease from affecting your smile is to practice excellent oral hygiene habits and attend routine dental exams and cleanings. Unfortunately, some people are simply more prone to periodontal issues. But a proper diagnosis can help prevent problems before they begin.
If you do develop gum disease, it is important that you continue to receive regular cleanings after your initial treatment is complete. While many dental patients have cleanings every six months, some require more frequent visits to effectively address the levels of oral bacteria present. Patients with a history of periodontal disease may benefit from cleanings every three to four months. Our team can also help you develop an at-home hygiene regimen that will be helpful for maintaining your progress between visits.
Learn More about How to Prevent Gum Disease
If you are experiencing bleeding, tender, or swollen gums, schedule a consultation at The Smile Center. We can help you prevent gum disease for a healthy smile. Call our office at (757) 473-8482 or contact us online anytime.


